Technical SEO involves improving your website for better search engine visibility. It includes making your site easier to find, understand, and store content. Additionally, it focuses on enhancing user experience, such as improving site speed and mobile-friendliness. By implementing technical SEO strategies effectively, you can optimize your website to rank higher in search results. In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn essential techniques and best practices to maximize your site’s technical SEO potential and drive organic traffic.


Technical SEO involves improving your website for better search engine visibility. It includes making your site easier to find, understand, and store content. Additionally, it focuses on enhancing user experience, such as improving site speed and mobile-friendliness. By implementing technical SEO strategies effectively, you can optimize your website to rank higher in search results. This comprehensive guide will teach you essential techniques and best practices to maximize your site’s technical SEO potential and drive organic traffic.
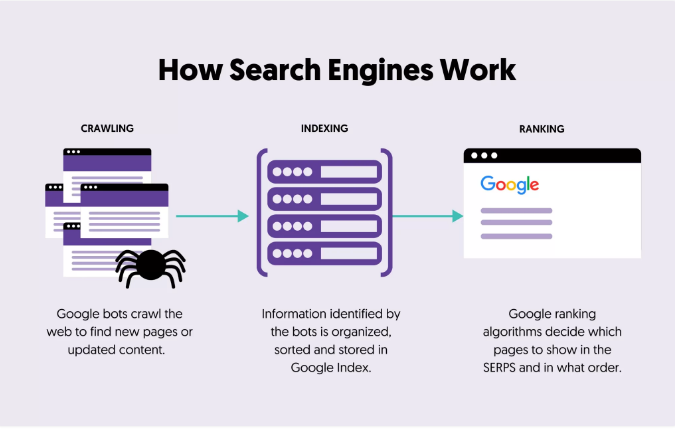
Crawling is an important part of how search engine’s function. It involves search engines following links on pages they already know about to discover pages they haven’t seen before.
For instance, we add new blog posts to our main blog page whenever we publish new blog posts. So, when a search engine like Google crawls our blog page, it notices the newly added links to the latest blog posts. This is one of the ways Google finds our new blog posts.
There are various methods to ensure your pages are accessible to search engines.
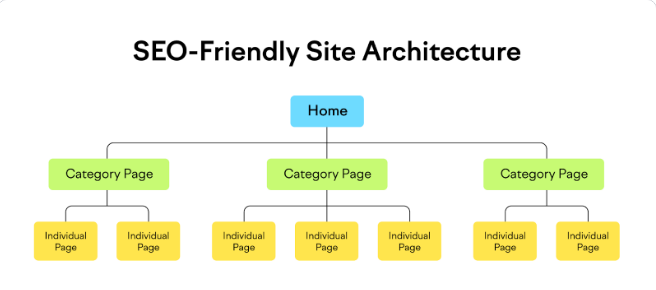
Site architecture, also known as site structure, refers to how pages are interconnected within your website. A well-organized site structure assists crawlers in swiftly locating your website content. Therefore, when structuring your site, ensure that all pages are easily accessible from your homepage with just a few clicks. In the site architecture depicted above, pages are arranged in a logical hierarchy. The homepage links to category pages, and these category pages, in turn, connect to individual subpages on the site. This layout also minimizes the presence of orphan pages. Orphan pages are pages lacking internal links, making it challenging, or sometimes impossible, for crawlers and users to discover them.
Using an XML sitemap is beneficial for helping Google locate your website’s pages. An XML sitemap is a file that contains a list of important pages on your site. It informs search engines about the pages you have and where to find them. This is especially useful if your site has many pages or if they are not well-connected
Below is an example of XML sitemap


Your website’s sitemap is typically found at one of these two URLs:
After locating your sitemap, submit it to Google through Google Search Console (GSC).Visit Google Search Console (GSC) and select “Indexing” from the sidebar. Then, click on Sitemaps.
Next, paste your sitemap URL into the provided field and click on the “Submit” button.
Once Google finishes processing your sitemap, you should receive a confirmation message similar to this:

After search engines check your pages, they aim to understand what’s on them. They store this information in their search index, a massive database with billions of webpages.For your webpages to show up in search results, they need to be indexed by search engines. One easy way to see if your pages are indexed is by using a “site:” search operator on Google.
When Google discovers similar content across multiple pages on your site, it may struggle to determine which page to prioritize in search results.Here’s where canonical tags become useful.
The canonical tag (Rel=”canonical”) specifies a link as the original version, signaling to Google the page it should prioritize for indexing and ranking.
This tag is placed within the <head> section of a duplicate page (although it’s advisable to include it on the main page too) and appears like this:

Creating a website structure that’s friendly to SEO, sending your sitemap to Google, and using no index and canonical tags appropriately can help ensure your pages are crawled and indexed.
But to fully optimize your site for technical SEO, consider these additional best practices:
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is a secure iteration of the standard Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP).
It serves to safeguard sensitive user data such as passwords and credit card information from potential compromises.
Since 2014, it has also served as a ranking factor.
To verify if your website uses HTTPS, simply visit it.
Look for the “lock” icon in the browser bar to confirm its usage
If you encounter the “Not secure” warning, it indicates that HTTPS is not being used on your website.
In this situation, it’s essential to install a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) certificate.
These certificates verify the website’s identity and establish a secure connection for users browsing the site.
Page speed influences rankings on both mobile and desktop devices.
To improve your site’s performance, ensure it loads quickly.
You can utilize Google’s Page Speed Insights tool to assess your website’s speed.
The tool provides a performance score ranging from 0 to 100, with higher scores indicating better performance.
Here are some additional tips to boost your website’s speed
Compress your images:
Images typically comprise the largest files on a webpage. Utilizing image optimization tools like Short Pixel can compress them, reducing their file sizes for faster loading times.
Use a content distribution network (CDN)
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) keeps copies of your webpages on servers across the globe. When someone visits your site, the CDN directs them to the nearest server, reducing the distance that the requested files need to travel.
Minify HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files
Minification involves removing unnecessary characters and whitespace from code, which helps to decrease file sizes. This improvement enhances page load time.
Google now prioritizes mobile-first indexing, meaning it primarily assesses the mobile versions of webpages for indexing and ranking content.
Ensure your website is optimized for mobile devices.
To confirm this, utilize the Page Speed Insights tool.
Once you’ve analyzed a webpage, navigate to the “SEO” section of the report and then to the “Passed Audits” section.
Here, you’ll discover if your site incorporates mobile-friendly elements or features:
Meta viewport tags: These provide instructions to browsers on how to control sizing for a page’s visible area.
Legible font sizes.
Adequate spacing around buttons and clickable elements.
Breadcrumb navigation, also called “breadcrumbs,” is a helpful trail of text links that guide users through a website, showing them their current location and the steps they took to get there.
For example:
These links make it easier to move around the website. Users can go to higher-level pages without needing to keep clicking the back button or dealing with complicated menus.
A robots.txt file informs Google about the sections of the site it’s allowed to access and those it should avoid.
Here’s an example of robots.txt file:
You can find your robots.txt file by adding “/robots.txt” to the end of your homepage URL. For instance, yoursite.com/robots.txt.
It’s important to check this file to ensure you’re not unintentionally preventing Google from accessing crucial pages using the disallow directive.

Drop us your inquiry our A-One web design and digital marketing agency knows the art of how to craft the diamond, Let’s Work and grow together.