What is SEO?
SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization. It refers to the process of enhancing your website’s visibility and ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs) organically, meaning without paying for placement. The goal of SEO is to drive more organic (non-paid) traffic to your website by improving its relevance and authority in the eyes of search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo.
Why SEO is a Big Deal for Businesses in Dubai
Digital marketing is becoming a must for businesses everywhere, and Dubai is no exception. Companies are spending more on online strategies, with a 13% rise in digital marketing budgets. At the heart of these strategies lies SEO—it’s the key to making your business stand out online and reaching the right audience.
How SEO Can Transform Your Business
SEO isn’t just about technical details; it’s about making your business easier to find online. Imagine being the first business customers see when they search for products or services you offer. That kind of visibility can make all the difference. Learning and using SEO effectively can give you a powerful advantage in today’s digital-first world.
Who Can Benefit from SEO?
Whether you’re running a business, working in marketing, or even looking for your next career move, understanding SEO can open doors. It’s a skill that helps you get ahead, find new opportunities, and connect with more people online.
Ready to make your business more visible and attract more customers in Dubai? Start with these simple but powerful SEO tips tailored just for you!
Learn How SEO Works to Boost Visibility and Drive Organic Traffic

1. Understand How Search Engines Work
In essence, to ensure your business is discoverable via search, across all platforms, it’s essential to grasp the technical workings of search engines and then make sure that you make it look effective. Provide all the right “signals” to do so.
When talking about traditional web search engines like Google, there are four distinct search phases:
- Crawling: Search engines use crawlers to find pages on the web by following links and using sitemaps.
- Rendering: Search engines generate how a page will look using HTML, JavaScript, and CSS information.
- Indexing: Search engines analyze the content and metadata of the pages they find and add them to the database (although there is no guarantee that every page on your website will be indexed).
- Ranking: Smart computer programs check lots of things to decide if a webpage is useful and good enough to show up when someone searches for something.
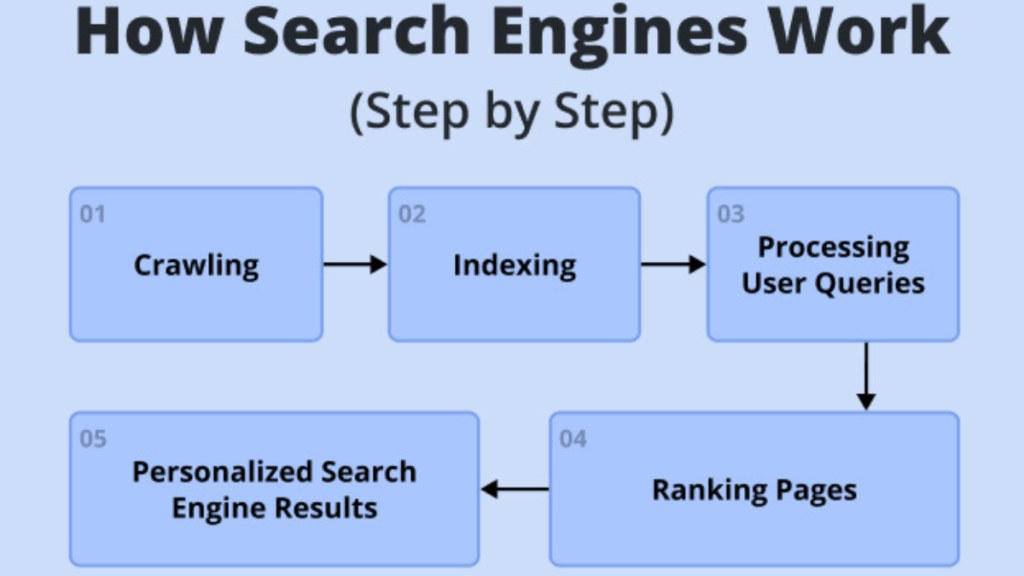
However, optimizing for Google search is different from optimizing for other platforms like YouTube or Amazon search.
Let’s take Facebook, for example, where factors such as engagement (likes, comments, shares, etc.) and people are connected to the topic. Then, on Twitter, signs like reviews, interactions, or author credibility are important.
And more complicated things: Search engines have added machine learning elements to stratify content – making it more difficult to say “this” or “that” resulted in good or bad performance.
2. Research

Research is a key part of SEO. Some types of research that improve SEO performance include:
- Audience Research: It is important to understand your target audience or market. Who are they (ie their demographics and psychographics)? What are their pain points? What questions do they have that you can answer?
- Keyword Research: This process helps you identify and include relevant and valuable search terms that people are using on your pages – and understand how much demand and competition there is to rank for those keywords.
- Competitor Research: What are your competitors doing? What are their strengths and weaknesses? What kind of content do they publish?
- Brand/business/customer research: What are their goals – and how can SEO help them achieve those goals?
- Website Research: Different types of SEO audits can highlight opportunities and issues on the website that are preventing success in organic search. Some research to consider: technical SEO, content, link profile, and E-E-A-T.
- SERP analysis: This will help you understand the search intent for a given query (for example, is it commercial, transactional, informational, or navigational) and create content that will gain rankings or views is more likely to do.
3. Planning

An SEO strategy is your long-term action plan. You need to set goals – and a plan for how you will reach them.
Think of it as a road map to your SEO strategy. The route you embark upon may evolve with time, yet the final destination ought to stay resolute and unwavering.”
Your SEO plan might include things like:
- Define and set meaningful KPIs and metrics.
- Deciding how projects are developed and implemented (internal, external, or mixed).
- Coordination and communication with internal and external stakeholders.
- Selection and implementation of tools/technology.
- Recruitment, training, and team building.
- Setting a budget.
- Measuring and reporting on results.
- Document strategy and process.
4. Creation and implementation

Once all the research is done, it’s time to turn ideas into action. ie:
- Creating new content: Advise your content team on what content needs to be created.
- Improvements of existing pages: including updating and improving content, adding internal links, adding keywords/topics/entities, or identifying other ways to improve it are included.
- Remove Old, Outdated or Quality Content: Content types that don’t rank well, drive traffic conversions or help you achieve your SEO goals.
5. Monitoring and Maintenance

You need to know when something goes wrong or breaks on your whole site or some part of your website. So Monitoring your site is important.
You need to know if traffic is dropping to critical pages, pages are slow, unresponsive or de-indexing, your entire website is going offline, links are breaking, or any other potentially catastrophic issues.
6. Performance analysis, evaluation and reporting
If you don’t measure SEO, you can’t improve it. To make informed decisions about SEO, you need to use:
- Website Analytics: Set up and use tools to collect performance data (at least free tools like Google Analytics, Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools).
- Tools and platforms: There are many”All in one” platforms (or suites) that offer multiple tools, but you can choose to only select SEO tools to track performance on specific tasks. Or, if you have the resources and none of the tools on the market do what you want, you can build your tools.
After you collect the data, you need to report on the progress. You can create reports using software or manually.
Performance reporting should tell a story and be done at reliable time intervals, especially when compared to past reporting periods (eg, year-over-year). This will depend on the type of website (usually, it will be monthly, quarterly, or some other interval).
Here are some Tips To Increase Your Business Website’s SEO:

- Keyword Research: Identify relevant keywords and phrases that potential customers might use to find your products or services. Use tools like Google Keyword Planner or SEMrush to research keywords with high search volumes and low competition.
- Optimize On-Page Elements: Ensure that your website’s title tags, meta descriptions, headings, and content include relevant keywords. Optimize images by using descriptive filenames and alt tags.
- Create High-Quality Content: Develop informative, engaging, and valuable content that addresses the needs and interests of your target audience. Regularly update your website with fresh content to keep it relevant and encourage return visits.
- Improve Website Loading Speed: Users and search engines prefer fast-loading websites. Optimise your site’s speed by compressing images, minifying CSS and JavaScript files, and leveraging browser caching.
- Mobile Optimization: Ensure that your website is mobile-friendly as more users access the internet via mobile devices. Use responsive design techniques to provide a seamless experience across different screen sizes.
- Build Quality Backlinks: Earn backlinks from reputable and relevant websites. Quality backlinks signal to search engines that your site is credible and authoritative. You can achieve this through guest posting, influencer outreach, or creating shareable content.
- Optimize for Local SEO: If you have a physical location or serve specific geographical areas, optimize your website for local search. This includes creating a Google My Business profile, optimizing location-based keywords, and getting listed in local directories.
- Improve User Experience (UX): A positive user experience not only keeps visitors engaged but also signals to search engines that your site is valuable. Ensure easy navigation, clear calls-to-action, and intuitive design.
- Regularly Monitor and Analyze Performance: Use tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console to track your website’s performance, identify areas for improvement, and monitor keyword rankings. Adjust your SEO strategy accordingly based on the insights gained.
Basic Elements of SEO

As you delve into the realm of digital marketing and SEO, you’ll encounter various terms and phrases that may seem unfamiliar. Amidst this jargon, having a concise glossary of SEO elements and terminology can be beneficial. Here are some of the most frequently used:
1. Audience:
The audience, sometimes called the target audience, “is a group of consumers characterized by behaviour and specific demographics. Target audiences are the pillars of many businesses that influence decision-making for marketing strategy, such as how to spend money on advertising, how to solicit customers, and even what product to create next. Determining the target audience will affect almost every other aspect of SEO.
2. Searcher intent:
This term is used interchangeably with user intent and visitor intent, and it refers to the intent of an online search. There are four types of auditor intent:
- Informative intent
- Intent of navigation
- Transaction intent
- Business audits
3. Keywords:
Keywords “Any search term entered into Google (or another search engine) has a results page where websites are listed.” The term is somewhat of a misnomer, as a keyword can be a single word or a phrase that contains several words.
Marketers utilise keywords to enhance website content, aiding in the elevation of site and page rankings.
4. Meta Descriptions:
Meta descriptions get a little more technical on the search engines, but they have a huge impact on SERPs. Meta description An HTML element that provides a summary of a web page.
A page’s meta description tag is displayed on a search engine results page (SERP) as part of a search pattern and is intended to give the user an idea of the content that is on the page and how it is viewed by them. Related to the search query.
5. Content:
As the name suggests, content refers to any written, audio, or visual material present on your website. Surprisingly, all of these aspects can benefit from SEO techniques. While “Content is king” may seem cliché in the realm of digital marketing, it holds. Content serves as the cornerstone of any website and should be the primary focus of SEO strategies and enhancements.
6. Backlinks:
Backlinks are sometimes referred to as inbound and outbound links and are part of an off-page SEO strategy. Backlinks are created when one website links back to another – to improve SEO, you want to have as many backlinks as you can. Backlinks show Google that you are an authority on a particular topic and essentially act as a “vote of confidence” from one website to another.
7. Site Structure:
Your website’s page hierarchy is carefully organised, reflecting its internal communication. This layout should facilitate easy information retrieval for users and aid search engine crawlers in grasping the connections between pages. Google and other search engines assess the organisation of your site, influencing its ranking. A user-friendly navigation system correlates with a higher rating.
8. Site Speed:
As the term suggests, site speed refers to “how rapidly users can view and engage with content.” As previously highlighted, the route from the user to your content should be as straightforward as feasible, with speed being a crucial factor. If your site loads slowly, loads incrementally or returns a 404 error message (the worst scenario), search engines will penalise you for it. Optimising search speed is a vital aspect of effective SEO and can determine whether you rank on page one or page two.
9. Schema:
Another technical aspect of SEO is schema. schema “is a structured data dictionary that helps search engines better understand the information on your website to provide richer results. This markup allows search engines to identify the entities mentioned on your site. See the meaning and connections behind it. For this reason, schema markup has become a hot topic in SEO.
Understanding Types of SEO

1. On-Page SEO
On-page SEO focuses on optimizing individual web pages to rank higher and earn more relevant traffic in search engines. It involves optimizing content, HTML source code, and website architecture. From crafting compelling meta tags to improving keyword placement, on-page SEO aims to enhance user experience and signal relevance to search engines.
- Domain names
- Page URLs
- Page titles
- Headers
- The main body text of each page
- Images
- Videos
- Alt text
- Navigational elements
- Meta description tags
- Internal links
- Sitemaps
2. Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO involves activities conducted outside of a website to improve its search engine rankings. This includes building backlinks, social media engagement, and online reputation management. Off-page SEO signals to search engines that a website is authoritative, credible, and trustworthy, thus boosting its visibility in search results.
- Link Building
- Social Media Engagement
- Online Reviews
- Guest Blogging
- Influencer Outreach
- Local SEO Strategies
3. Technical SEO
Technical SEO focuses on optimizing the technical aspects of a website to improve its crawling, indexing, and overall search visibility. This includes optimizing site speed, fixing crawl errors, implementing structured data markup, and ensuring mobile-friendliness. Technical SEO lays the foundation for effective on-page and off-page optimization, ensuring that search engines can access and understand the content.
- Canonicalization
- XML Sitemap
- Robots.txt
- Schema markup
- Structured data
- URL structure
- Meta tags
- Alt attributes
- Page speed optimization
- Mobile responsiveness
- Internal linking
- HTTPS implementation
- Crawlability
- Indexability
4. Local SEO
Local SEO targets geographically specific searches to promote businesses, products, and services to local customers. It involves optimizing online presence for local searches, managing online reviews, and claiming and optimizing Google My Business listings. Local SEO is essential for brick-and-mortar businesses seeking to attract customers in their vicinity.
5. Voice Search SEO
Voice search SEO focuses on optimizing content to cater to voice search queries made through virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant. It involves understanding natural language patterns, providing concise answers to common questions, and optimizing content for featured snippets. Voice search SEO is becoming increasingly important as the popularity of voice-enabled devices continues to rise.
6. E-commerce SEO
E-commerce SEO is tailored to online retailers aiming to improve visibility and drive sales through search engines. It involves optimizing product pages, enhancing user experience, and implementing structured data markup for product information. E-commerce SEO strategies aim to increase organic traffic, improve conversion rates, and boost revenue.
- Keyword Research
- On-Page Optimization
- Product Descriptions
- Category Page Optimization
- URL Structure Optimization
- Image Optimization
- Mobile Optimization
- User Experience (UX) Improvement
- Site Speed Optimization
- Schema Markup Implementation
- Internal Linking Strategy
- Content Marketing
- Blogging for SEO
- Social Media Integration
- Review Management
- Local SEO
- Backlink Building
- Competitor Analysis
- E-commerce Platform Optimization
- Analytics and Reporting
7. Mobile SEO
Mobile SEO focuses on optimizing websites for mobile devices to provide a seamless browsing experience for mobile users. It includes ensuring mobile responsiveness, optimizing page speed, and prioritizing mobile-friendly content. With the majority of internet users accessing websites via mobile devices, mobile SEO is essential for maintaining competitiveness in search rankings.
8. Video SEO
Video SEO involves optimizing video content to improve its visibility and ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs). This includes optimizing video titles, descriptions, tags, and thumbnails, as well as enhancing user engagement metrics such as watch time and click-through rate. Video SEO is crucial for businesses leveraging video marketing to reach their target audience effectively.
9. Image SEO
Image SEO focuses on optimizing images to improve their visibility in image search results and enhance overall website SEO. This includes optimizing image filenames, alt text, captions, and file sizes, as well as utilizing structured data markup for images. Image SEO not only improves the accessibility and user experience of a website but also drives additional organic traffic through image searches.
10. International SEO
International SEO, also known as global SEO, involves optimizing websites to target audiences in multiple countries and languages. It includes implementing tags, optimizing content for different languages and regions, and managing international targeting settings in the search console. International SEO enables businesses to expand their reach globally and effectively target diverse audiences.


